
Table of Contents
Published on: June 18, 2024
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, effective supply chain management has become a critical factor in determining a company’s success. The global market for traceability technology is projected to reach around $20.7 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 14.3% during the forecast period.
Traceability – the ability to track the movement and location of products throughout the entire supply chain is a key aspect of supply chain management. Traceability is not only important for ensuring product quality and safety, but it also plays a crucial role in channel performance management (CPM). A study found that 75% of consumers are willing to switch to brands that provide more detailed product information, including traceability data.
Here, you can refer to the Traceability Format:
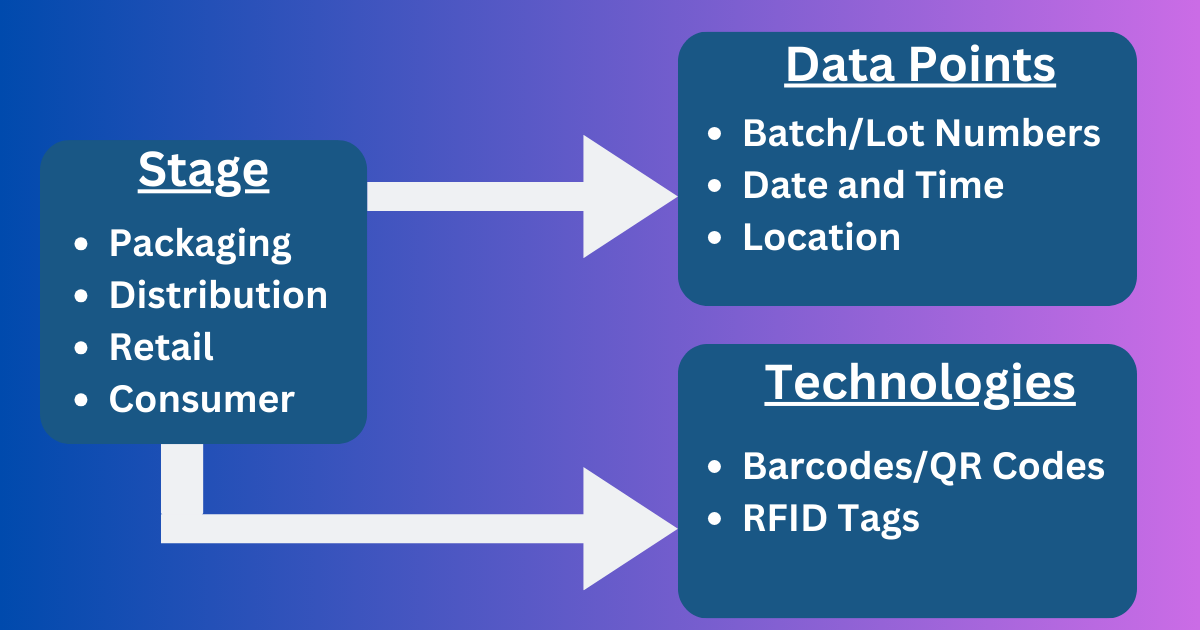
As the market for traceability solutions continues to grow, businesses are investing more in these technologies to ensure product safety, quality, and compliance. Channel performance management is the process of monitoring and optimizing the performance of various distribution channels to maximize overall business success. Traceability is a key parameter in this process, as it provides valuable insights into the movement and handling of products across different channels.
What is end-to-end traceability?
End-to-end traceability refers to the ability to track a product’s journey from the packaging to the final delivery to the customer. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 10% of medicines in low- and middle-income countries are counterfeit, driving the demand for improved traceability systems.
By having a comprehensive view of the entire supply chain, businesses can identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and ensure compliance with industry regulations and customer requirements.
Why is product traceability in manufacturing important to implement?
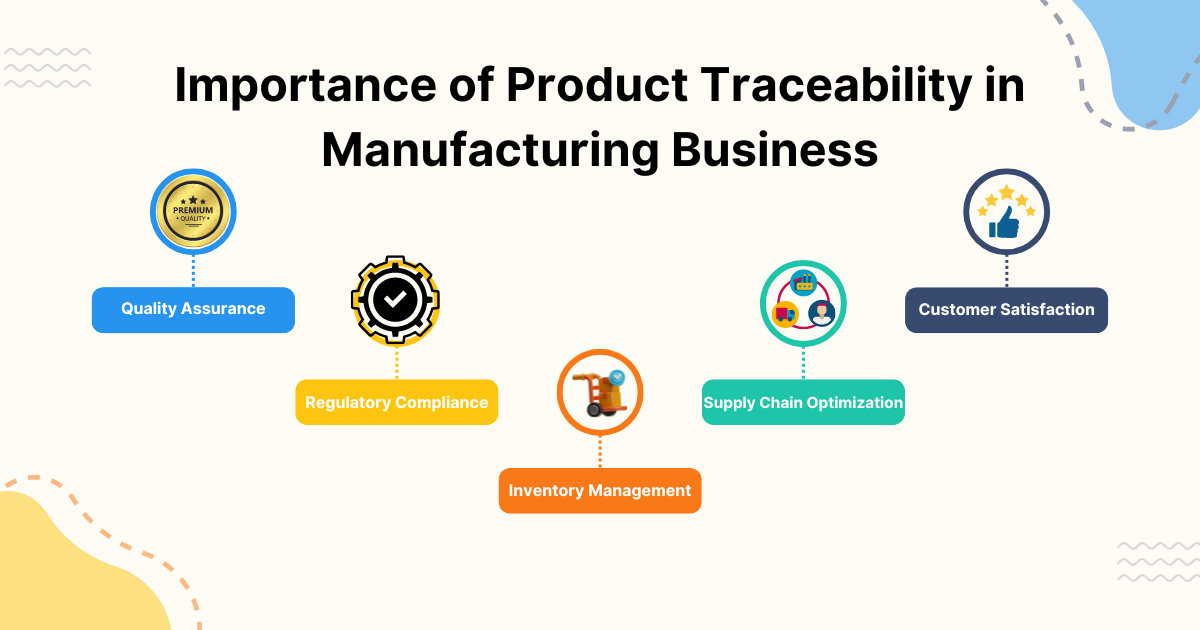
In a survey conducted by the International Trade Centre, 85% of companies identified traceability as a critical issue in their supply chains. Implementing product traceability in manufacturing offers several key benefits:
- Quality Assurance: Traceability helps manufacturers identify and isolate quality issues, enabling them to quickly address problems and prevent the distribution of defective products.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries, such as food, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices, have strict regulations regarding product traceability. Compliance with these regulations is essential to avoid costly penalties and maintain a good reputation.
- Inventory Management: Traceability data can provide valuable insights into inventory levels, stock movement, and product expiration dates, allowing manufacturers to optimize their inventory and reduce waste.
- Supply Chain Optimization: By tracking product movement and identifying inefficiencies, manufacturers can streamline their supply chain processes, reduce costs, and improve overall operational efficiency.
- Customer Satisfaction: Traceability enables manufacturers to provide customers with detailed information about the origin and journey of their products, fostering trust and transparency.
How to Track Production in Manufacturing?
Implementing traceability solutions can reduce production downtime by up to 50%, as manufacturers can quickly identify and address issues in the supply chain. Tracking production in manufacturing can be achieved through various methods and technologies, including:

- Barcode Scanning: Barcodes are widely used to track and identify products, components, and materials throughout the manufacturing process.
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID): RFID tags attached to products or packaging can be scanned, providing real-time data on the location and status of products.
- QR Codes (Quick Response Codes): These are two-dimensional barcodes that can store a significant amount of data, including text, URLs, or other information. In manufacturing, QR codes can be scanned to reveal details about the product’s journey through the production line, its specifications, and even its destination after leaving the factory. They are particularly useful because they can be scanned quickly and from any angle, which is ideal for fast-paced production environments.
Tracking and Tracing: 2 Sides of The Same Issue
Tracking and tracing are integral components of modern supply chain management, ensuring the visibility and accountability of products as they move from origin to destination. While they are often discussed together and share similarities, they address different aspects of supply chain visibility and management.
![]()
Tracking refers to the process of monitoring the progress and location of finished goods as they move through the supply chain in real-time or near-real-time. While Tracing involves identifying the historical path of a product, including its origins, processing steps, and any transformations it has undergone.
Tracking improves operational efficiency, reduces delays, and enhances customer satisfaction by providing up-to-date information on product locations. While tracing ensures regulatory compliance, supports quality assurance, and facilitates swift and effective recall processes by providing detailed historical records.
How to Improve Traceability?
To improve traceability in manufacturing, businesses can implement the following strategies:
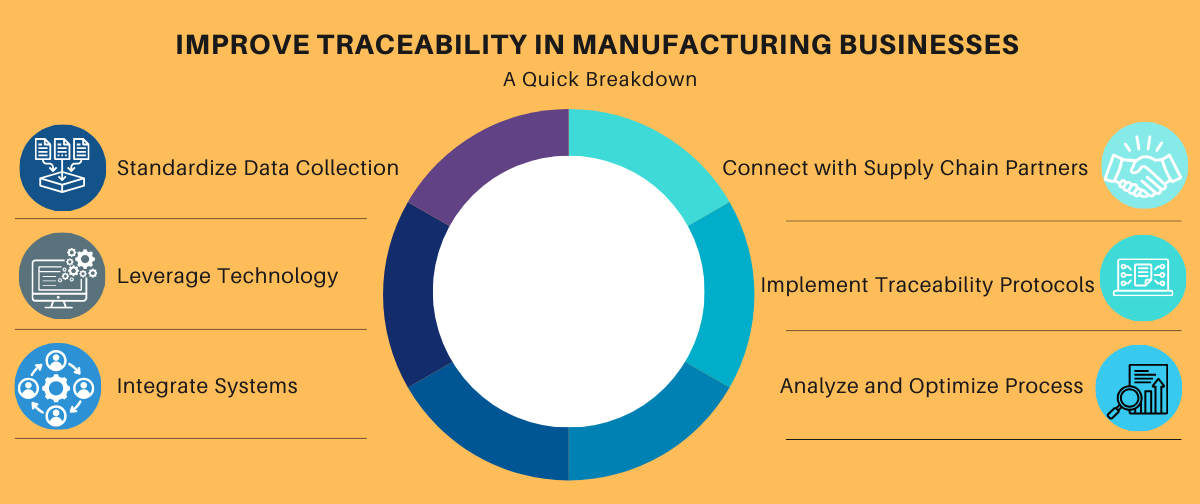
- Standardize Data Collection: Establish a consistent and comprehensive system for data collection, ensuring that all relevant information is captured and stored in a centralized database.
- Leverage Technology: Invest in advanced technologies, such as barcoding QR Codes and RFID, to automate the data collection and tracking processes.
- Integrate Systems: Ensure seamless integration between various systems, such as ERP, warehouse management, and transportation management, to create a holistic view of the supply chain.
- Collaborate with Supply Chain Partners: Foster strong partnerships with suppliers, and distributors to enhance end-to-end traceability and transparency.
- Implement Traceability Protocols: Develop and enforce clear protocols for product identification, labelling, and handling to ensure consistent traceability practices across the organization.
- Analyse and Optimize: Regularly review traceability data to identify areas for improvement, optimize processes, and make informed decisions to enhance overall supply chain performance.
Case Studies About Traceability in The Pharmaceutical Industry
The global pharmaceutical track and trace solutions market size is expected to reach $6.1 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 20.9%.
Cipla Limited, a prominent pharmaceutical company in India, undertook the initiative to implement a comprehensive traceability system to combat the challenges of counterfeit drugs, meet stringent regulatory requirements, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency. With its extensive product portfolio and global reach, Cipla needed a robust system to ensure product safety and regulatory compliance.
Challenges:
- Data Management: The analysis of inaccurate or irrelevant data, along with the storage and access of massive amounts of data, can lead to a decline in overall supply chain performance and efficiency.
- Technological Advancements: Keeping up with technological advancements and integrating them into the supply chain to improve efficiency and performance is a constant challenge.
- Unpredictability and Volatility: Persistent unpredictability in the market, labor shortages, and global bottlenecks are critical challenges that supply chains must navigate.
- Sustainability: Incorporating sustainable practices into the supply chain is becoming increasingly important and can be challenging to implement effectively.
Technological Solutions:
- Serialization: By implementing serialization for product lines, assigning a unique identifier to each package in the form of a 2D barcode or QR code. This code contains detailed product information such as product code, batch number, and expiration date.
- Barcodes: Barcodes have been the backbone of inventory management since their inception in the 1970s. These one-dimensional (1D) symbols encode data by varying the spacings and widths of parallel lines. They are cost-effective and widely used for managing large volumes of products, allowing for quick scanning and identification of items within a supply chain.
- QR Codes: Quick Response codes, are two-dimensional (2D) matrix barcodes that can store significantly more information than traditional barcodes – up to 7,089 numeric characters compared to barcodes’ of 20-25. This capacity enables QR codes to hold a wealth of data, including URLs, serial numbers, and even images, which can be accessed with a simple scan using a smartphone or dedicated scanner.
- RFID Technology: RFID tags are used to monitor the products’ movement in real-time. These technologies help ensure that products are stored and transported under optimal conditions.
At Last:
Traceability is a vital component of modern supply chain management, especially in industries where product safety and regulatory compliance are paramount. By leveraging advanced technologies and fostering collaboration across the supply chain, companies can enhance product safety, improve operational efficiency, and build consumer trust. The benefits of traceability extend beyond compliance, offering significant advantages in quality control, risk management, and brand reputation.

















